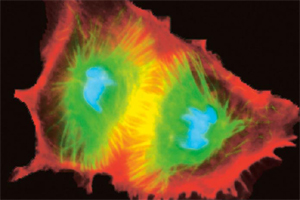
Cells are not formed spontaneously, they come from a stem or parent cell.
Eukaryotes have the capacity to split, transferring their characteristics and originating two daughter cells. This process is known as mitosis and it endures growth, renovation and cellular reparation, processes which are fundamental in order to continue living. The interval between each mitotic division is called the cell cycle.
The mitosis division process has the following steps (including a previous step):
– Interphase: this is a resting (prior) phase, during which the cell duplicates its genetic material and prepares for mitosis.
– Prophase: this is the first phase of mitosis, and during this stage the centriole (cylindrical structure that is part of the cytoskeleton) duplicates and each new centriole heads towards the poles of the cell. Chromosomes condense and the cell membrane begins to disintegrate. .
– Metaphase: in this stage, the pairs of chromosomes line up with the fibers of the spindle apparatus and are arranged in the center of the cell.
– Anaphase: a complete set of chromosomes manage to group together at each of the poles of the cell.
– Telophase: the nuclear membrane is formed once again around each set of chromosomes. They develop further, and two nuclei appear that are the same as the original.